Researchers have developed a battery that has a high voltage and will last a longer time than current tech.
Scientists have come up with a vitamin powered phone battery technology that will allow devices to last longer while giving them more voltage. Moreover, this could be an important step toward reducing the price tag of battery powered devices.
This new battery technology is not entirely unlike lithium-ion but are different in an important way.
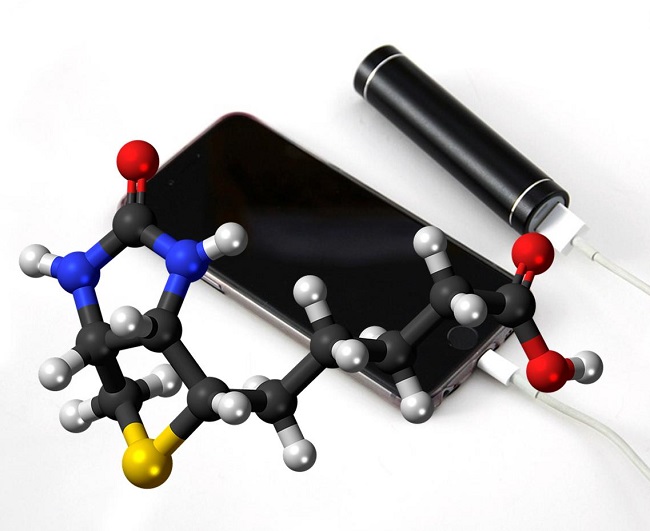
The battery is different because it uses flavin – a component of vitamin B2 – as its cathode. The cathode is the part of the battery that stores the electricity. Then, that energy can be used once it is connected to a device. This vitamin powered phone battery provides a more natural solution to the question of how to keep devices charged.
 Dwight Steferos from Canada’s University of Toronto, said “We have been looking to nature for a while to find complex molecules for use in a number of consumer electronics applications.” He added, “When you take something made by nature that is already complex, you end up spending less time making new material.”
Dwight Steferos from Canada’s University of Toronto, said “We have been looking to nature for a while to find complex molecules for use in a number of consumer electronics applications.” He added, “When you take something made by nature that is already complex, you end up spending less time making new material.”
The vitamin powered phone battery provides a very affordable way of giving mobile devices the charge they need.
This is not the first time a battery has been made with bio-derived components. However, this is the first rechargeable battery using bio-derived polymers. Polymers are long chain molecules. They are used for one of this new battery technology’s electrodes.
This technology’s key is the possibility it opens for keeping the energy stored within a vitamin-created plastic. The plastic is far less expensive than traditionally-used metals such as cobalt. The vitamin-created plastic is also more environmentally friendly and easier to process. It may play a central role in reducing our dependence on portable battery packs due to inadequate charge.
The scientists developed the material from vitamin B2. They sourced the vitamin from genetically-modified fungi. They used a semi-synthetic process for polymer preparation. It linked a long-chain molecule with two flavin units.
The result is a vitamin-powered phone battery that is environmentally friendly with a high voltage and with a high capacity. These and the rest of the findings from the researchers were published in the Advanced Functional Materials journal.
While AR technology has been developed to help to promote road safety, it could be causing the opposite result.
According to the results of preliminary studies on the use of augmented reality head up displays (HUDs) that show images on windshields that are meant to help to make driving safer and easier for motorists, the use of this technology could actually be making driving less safe.
The problem with AR technology while driving primarily involves distraction due to divided attention.
According to Ian Spence, a professor of psychology at the University of Toronto, “Drivers need to divide their attention to deal with this added visual information.” He also pointed out that “Not only will drivers have to concentrate on what’s happening on the road around them as they’ve always done, they’ll also have to attend to whatever warning pops up on the windshield in front of them.”
The professor ran the augmented reality display tests with two of his students to better understand the visual data.
 Spence worked with Sijing Wu and Yuechuan Sun, two of his students, in designing tests that would be able to measure the impact of displaying the additional information as an overlay on the reality seen by a driver. At first, the participants in the research were asked to complete a series of computer based trials. Within those trials, they reported several randomly arranged numbers (which ranged from one through nine) that were displayed on the screen. They needed to identify them as rapidly and accurately as possible once they were prompted to do so.
Spence worked with Sijing Wu and Yuechuan Sun, two of his students, in designing tests that would be able to measure the impact of displaying the additional information as an overlay on the reality seen by a driver. At first, the participants in the research were asked to complete a series of computer based trials. Within those trials, they reported several randomly arranged numbers (which ranged from one through nine) that were displayed on the screen. They needed to identify them as rapidly and accurately as possible once they were prompted to do so.
In some of the trials, they were also presented with a black-outlined square in order to provide a secondary form of stimulus. Those that received that additional stimulus were asked to report whether or not they had seen it. The numbered spots and the shape were displayed at the same time, and the shape appeared in only some trials in an unpredictable pattern among the participants.
When the squares were absent, the accuracy was quite high, which indicated that there wasn’t a lot of attention required in order to identify whether or not the square had appeared. However, when the square appeared along with the numbered spots, the average rate of missing it was one in 15. The higher the number of spots, the greater the average rate of missing the square. This indicated that if the user’s attention is occupied by additional information such as that displayed in augmented reality, it will also be increasingly distracted from the primary task, such as driving.
 Dwight Steferos from Canada’s University of Toronto, said “We have been looking to nature for a while to find complex molecules for use in a number of consumer electronics applications.” He added, “When you take something made by nature that is already complex, you end up spending less time making new material.”
Dwight Steferos from Canada’s University of Toronto, said “We have been looking to nature for a while to find complex molecules for use in a number of consumer electronics applications.” He added, “When you take something made by nature that is already complex, you end up spending less time making new material.”
 Spence worked with Sijing Wu and Yuechuan Sun, two of his students, in designing tests that would be able to measure the impact of displaying the additional information as an overlay on the reality seen by a driver. At first, the participants in the research were asked to complete a series of computer based trials. Within those trials, they reported several randomly arranged numbers (which ranged from one through nine) that were displayed on the screen. They needed to identify them as rapidly and accurately as possible once they were prompted to do so.
Spence worked with Sijing Wu and Yuechuan Sun, two of his students, in designing tests that would be able to measure the impact of displaying the additional information as an overlay on the reality seen by a driver. At first, the participants in the research were asked to complete a series of computer based trials. Within those trials, they reported several randomly arranged numbers (which ranged from one through nine) that were displayed on the screen. They needed to identify them as rapidly and accurately as possible once they were prompted to do so.